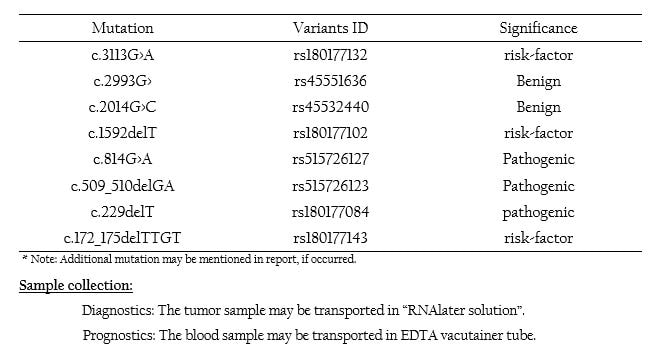
PALB2 Mutation Panel
PALB2 Overview:
- PALB2 is abbreviated as Partner And Localizer of BRCA2[1].
- PALB2 goes in hand with the BRCA genes during the process of DNA damage response [1].
- PALB2 was initially detected as a BRCA2 interacting protein which acts as an important key for BRCA2 genome functions [2&3], which also interacts with BRCA1 [4].
- The cells which are lacking PALB2 may lack in BRCA1/2 dependent DNA repair pathway [2&3].
- Thus, the inactivation of this PALB2 gene may result in the inactivation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 which are the important genes for causing breast and ovarian cancer.
- The occurrence of PALB2 mutations is very rare but is considered as one of the important factors in human Ovarian cancer [5].
- Mutations in PALB2 may at times lead to a defective DNA repair[1].
- PALB2 germline mutations results in losing the genome stability which results in inducing cancer onset and progression through the accumulation of defects in DNA [6].
- Heterogenous nature of PALB2 germline mutation may cause DNA replication and DNA damage response [7].
- Though the occurrence of PALB2 mutations are rare, it is roughly estimated that there is an increased risk of this particular mutation when compared to BRCA2 mutations [8].
- The biallelic germline mutation and loss of function in PALB2 gene is also known to cause a condition called Fanconi’s anaemia (FA) [5].
- PALB2 mutations is also associated with the ovarian cancer susceptibility [9].
- Monoallelic mutations of PALB2 is associated with an elevated susceptibility of ovarian cancer[10].
- Though its occurrence is found to elevate, this gene is denoted as moderate penetrance in breast and ovarian cancer gene compared to other genes [11].
- PALB2 mutations must be encouraged in women who have genetically inherited Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) in case of a strong familial history for cancer[11].
- PALB2 mutations can also be found in 1-4% of families having negative BRCA mutations[8].
- The risk of PALB2 mutation is twice or thrice higher the women above 55 years of age and four times higher for women above the age group of 80.[12].
- In case of cancer occurrence without family history, the risk of breast cancer in women with PALB2 mutation until up to age of 70 is nearly 33%
- There is an estimated risk of 58% breast cancer occurrence in women with PALB2 mutation having family history of cancer [13].
- PALB2 deficient cells are sensitive to PARP inhibitors[14].
- Additional to Ovarian cancer, PALB2 mutation have increased the risk of Breast, prostrate and pancreatic cancer[5].
- PALB2 mutation has a great influence in case of familial inheritance of pancreatic cancer[15].
- Apart from the above-mentioned cancer types, PALB2 has an increased possibility in causing melanoma due to an increase in BRCA2 mutation carriers.
- Apart from cancer, mutation in this gene also causes Fanconi’s anaemia (FA) as PALB2 is one of the two important genes causing FA.
- PALB2 along with BRCA2 also show an elevated risk to childhood solid tumor with bi-allelic mutation carrier[15].
- PALB2 mutations may also rise in BRCA1/2 negative patients those have BRCA2 like cancer phenotype (i.e.,) BRCA2 associated tumors.
- Pauty J, et al, (2014). Biochem J, 461.
- Xia B, et al. (2006). Mol Cell, 22:719–29,
- Sy SM, et al., (2009). J Biol Chem, 284:18302–10.
- Zhang F, et al., 2009
- Tischkowitz, and Xia B. (2010). Cancer Res, 70:7353-7359.
- Nepomuceno TC, (2017). Int J Mol Sci, 18.
- Nicola Waddel MP, et al., (2015). Nature, 518:495e501.
- Poumpouridou N and Kroupis C. (2012). Clin Chem Lab Med, 50:423e34.
- Walsh T, et al., (2011). Proc Natl Acad Sci, 108:18032e7.
- Cybulski C, et al., (2015). Lancet Oncol, 16(6):638-644.
- Velázquez C., et al., (2019). The Breast, 43: 91-96.
- Casadei S, et al., (2011). Cancer Res, 71(6):2222-2229.
- Wesoła M, and Jeleń M. (2017 ). Adv Clin Exp Med. 26(2):339-342.
- Buisson R, et al., (2010). Nat Struct Mol Biol, 17(10):1247-1254.
- Jones S, et al., (2009). Science 324:217.